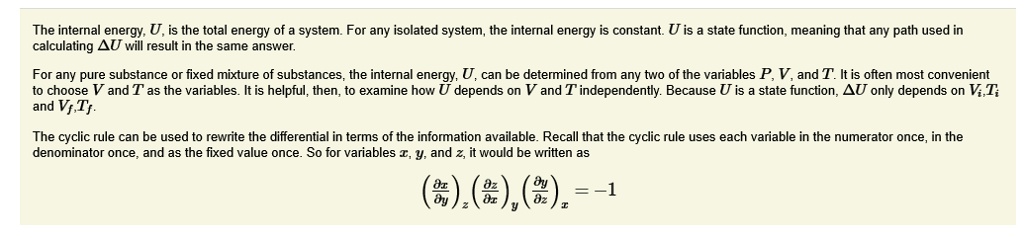
What Is The Total Energy Of A System
What is the total energy of a system. Therefore the total energy of the system is 1110 7 Joules. You can compute the total energy based on the known attributes mentioned in the total energy equation. Because the particles in an ideal gas do not interact this system has no potential energy.
Since the system is initially at rest the total energy is just the potential energy of the compressed spring. In thermodynamics the enthalpy is the measure of energy in a thermodynamic system. The internal energy of a system can be understood by examining the simplest possible system.
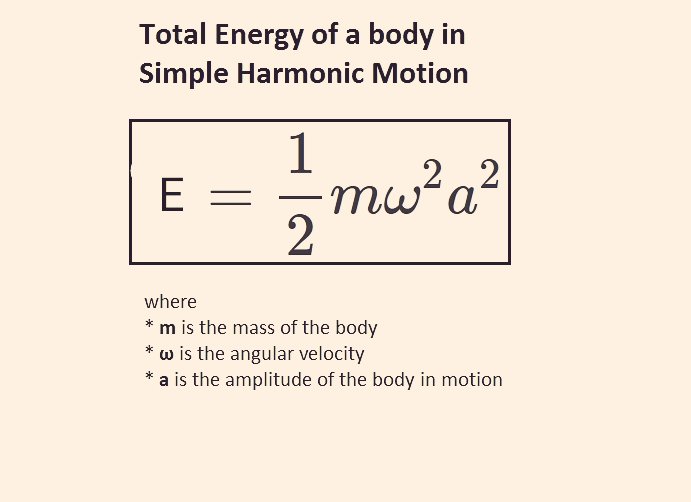
The position of y B y B is half of the position at y C y C or -020 m -020 m. The mass of the block is the weight divided by. The total energy in the system however remains constant and depends only on the spring contant and the maximum displacement or mass and maximum velocity v m ωx m The movie at right 25 KB Quicktime movie shows how the total mechanical energy in a simple undamped mass-spring oscillator is traded between kinetic and potential energies while the total energy remains constant.
The Attempt at a Solution. Internal energy represents the molecular energy of a system and. Centre of mass KE.
What is the total amount of potential and kinetic energy in a system. Where m is the mass of the particle and K is a constant called. 780 5 cos20 3665 - 20581607J.
This follows from the additive property of the dot product in the expression for the work done Lets look at some specific examples of types of potential energy discussed in Work. What you do is you add up all the energy and the result is the total energy. One of the thermodynamic properties of a system is its internal energy E which is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of the particles that form the system.
The total mechanical energy of the spring-mass system is given by E 1 2 m ω 2 A 2. The total energy at that point is therefore just the kinetic energy of the moving mass.
Because the particles in an ideal gas do not interact this system has no potential energy.
Of centre of mass Heres the derivation from my book. Total energy is the sum of all or combination of different forms of energy that exist around the system. Total energy textbf total energy total energy. The author starts off by deriving the individual momenta of the two particles wrt. It is the thermodynamic quantity equivalent to the total heat content of a system. The force you exert on the chair contributes to the overall change in kinetic energy of the system the chair with a positive amount and therefore does positive work on the system. Centre of mass KE. This follows from the additive property of the dot product in the expression for the work done Lets look at some specific examples of types of potential energy discussed in Work. E T 12000kg 98Nkg 95m E T E P.
The author starts off by deriving the individual momenta of the two particles wrt. The Hamiltonian of a system is equivalent to the total energy of the system if and only if the following conditions are satisfied. Solution Since the total energy of the system is zero at point A as discussed previously the maximum expansion of the spring is. The total energy of a mechanical system is always conserved under elastic collisions. It is what it says. Centre of mass KE. The author starts off by deriving the individual momenta of the two particles wrt.




























Post a Comment for "What Is The Total Energy Of A System"